If your employees are covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act, you should be aware of a change which may significantly increase your payroll costs by increasing the number of employees who are eligible for mandated overtime pay.
On April 23, 2024, the U.S. Department of Labor announced a final rule, Defining and Delimiting the Exemptions for Executive, Administrative, Professional, Outside Sales, and Computer Employees, which became effective July 1, 2024.
By law, all U.S. employees covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) are subject to minimum wage and overtime compensation, unless they are exempt under the FLSA’s “EAP” exemption. To qualify for the EAP exemption an employee must:
- be paid a salary, a predetermined and fixed amount that is not subject to reduction because of variations in the quality or quantity of work performed;
- be paid at least a specified weekly salary level; and
- primarily perform executive, administrative, or professional duties, as provided in the Department’s regulations.
Before July 1, 2024, if the employee met the criteria in #1 and #3, they must have earned a minimum of $684 per week (the equivalent of $35,568 per year) to be considered exempt from FLSA mandated overtime pay.
Effective July 1, 2024, to remain exempt, these qualified salaried employees must earn at least $844 per week (the equivalent of $43,888 per year).
The pay threshold increases again effective January 1, 2025 to $1,128 per week (equivalent to $58,656 per year).

The standard salary will then be subsequently re-evaluated on July 1, 2027 and every 3 years thereafter.
The Department’s regulations also provide an alternative test for certain “highly compensated” employees who are paid a salary, earn above a higher total annual compensation level, and satisfy a minimal duties test.
A highly compensated employee is deemed exempt under Section 13(a)(1) if:
- The employee earns a total annual compensation of $107,432 or more, which includes at least $684 per week paid on a salary or fee basis;
- The employee’s primary duty includes performing office or non-manual work; and
- The employee customarily and regularly performs at least one of the exempt duties or responsibilities of an exempt executive, administrative or professional employee.
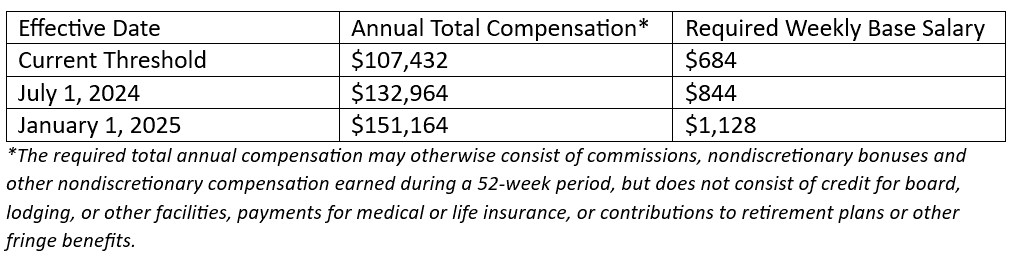
Before July 1, the threshold for the qualified highly compensated employee exemption was $107,432 per year, including at least $684 per week paid on a salary basis.
Effective July 1, 2024 the threshold increased to $132,964 per year, including at least $844 per week paid on a salary or fee basis.
As of January 1, 2025 the total compensation threshold becomes $151,164 per year, including at least $1,128 per week paid on a salary or fee basis.
The threshold for the highly compensated employee total annual compensation will be subsequently re-evaluated as of July 1, 2027 and every three years thereafter.
This information is not a complete summary of the complexities of the Fair Labor Standards Act. It is meant rather to make you aware of certain changes which may apply to your employees. Additionally, you should continue to monitor the FLSA for other changes or updates. If you have questions about the Fair Labor Standards Act and how it relates specifically to your circumstances, we encourage you to reach out to your legal representation for additional clarification.
